Converse of a conditional statement
The converse of a conditional statement switches the hypothesis and the conclusion.
Example #1
Conditional statement : If a polygon has four sides, then it is a quadrilateral.
Converse: : If a polygon is a quadrilateral, then, it has four sides.
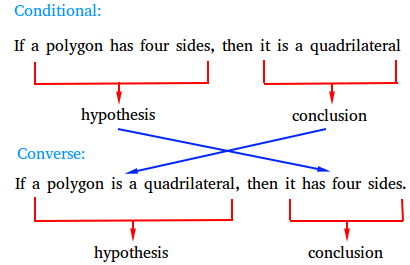
Notice that both the conditional statement and the converse are true.
Example #2
Conditional statement: If you are a vegan, then you do not eat meat.
Converse: If you do not eat meat, then you are a vegan.
Notice that the conditional statement is true, but the converse is false.
The converse is false because may be you eat poultry or seafood.
Example #3
Conditional statement: If you add 5 and and 10, then you get a sum of 15.
Converse: If you got a sum of 15, then you added 5 and 10.
Notice that the conditional statement is true, but the converse is false.
The converse is false because you can also add 4 and 11 to get a sum of 15..